Historical Timeline
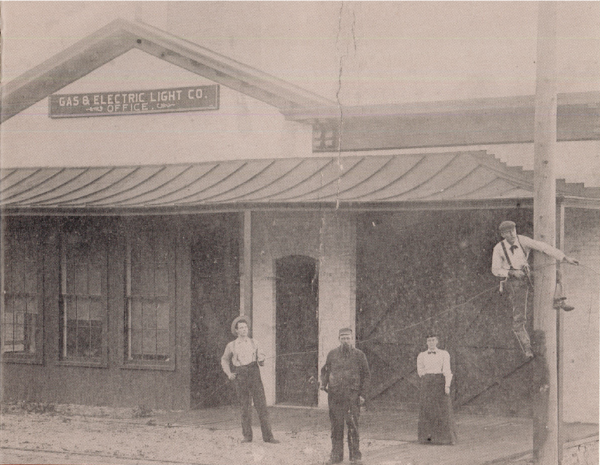

September 1896

1911
Net book Value – The utility was appraised at a net book value of $25,244.33. Additional equipment was added as needed.
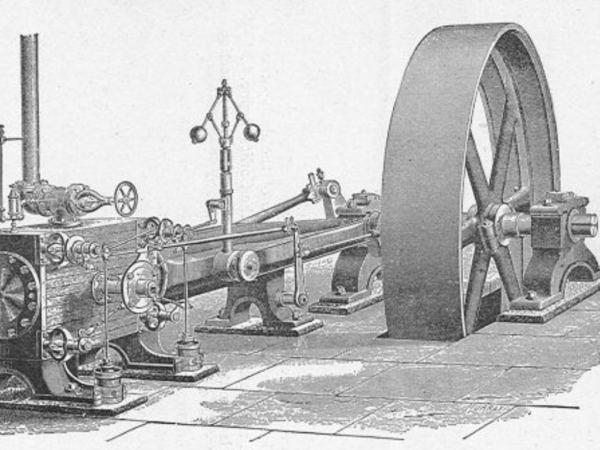
1915
Steam engine replaced – The original steam engine is replaced by a 500kw turbine and other additions are made.
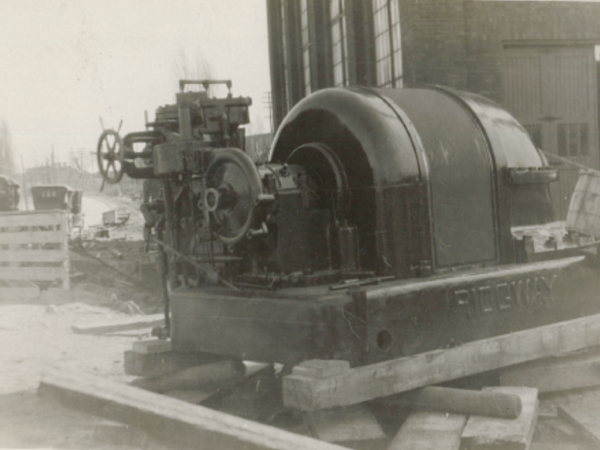
1917
Turbine & Boiler – A 1000 kw turbine and boiler are installed.
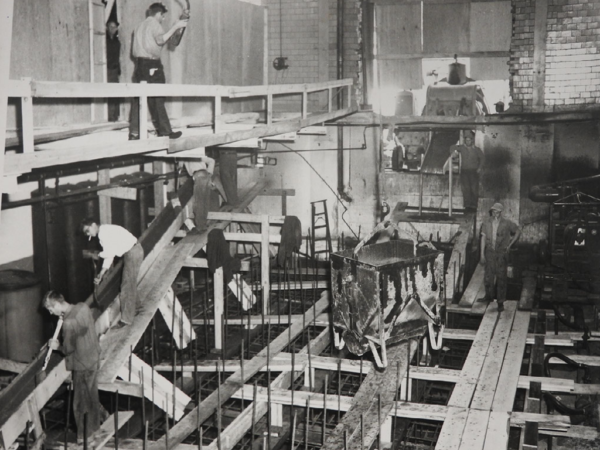
1924
NEW Boiler Room – Work begins on construction of a new boiler and the addition of a new 1500 kw turbine. Total cost $110,356.
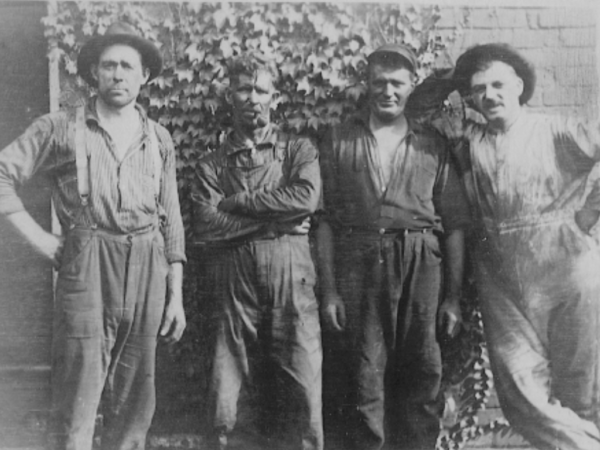

1927
System Upgrades – Additional equipment is installed, consisting of a 500-hp boiler and stoker, a Zeolite water softening system, boiler feed pumps, and a complete coal conveying system at a cost of $54,589.
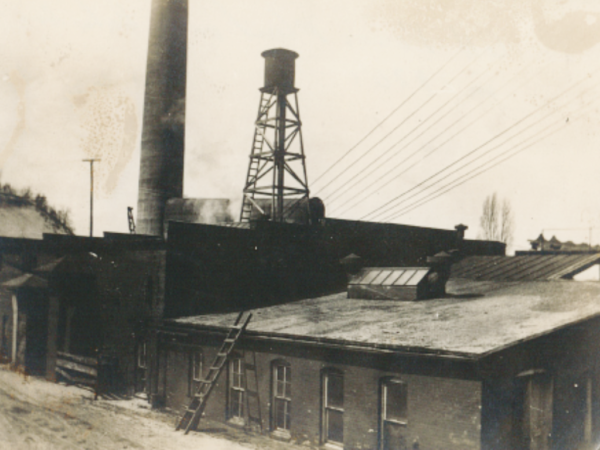

1929
Construction of a Diesel Generator Plant – In response to system growth, the City begins constructing a diesel generator plant. Work was suspended temporarily in early 1930 when Consumers Power Company offers $1,200,000 for the system. The offer was turned down and a Board of Public Works was created during the same election.

1930
Construction resumes on Diesel Plant – Construction of the diesel plant resumes after April 1930 election. Two 1150-hp DeLaVergne 6-cylinder engines connected to 800kw Elliot generators with direct connect exciters are purchased and installed. Project cost $217,000.
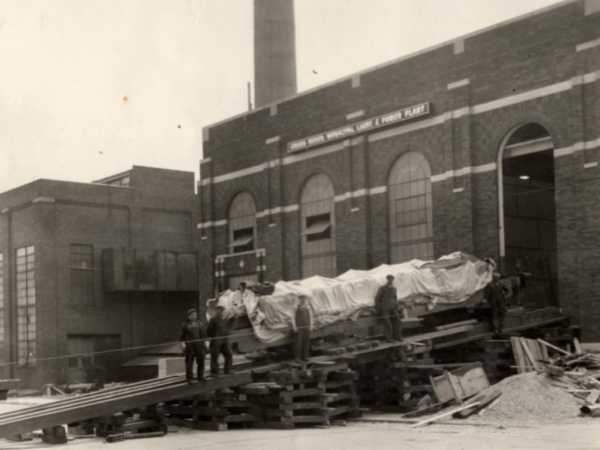

1934
DeLaVergne Diesel Engine – A third identical DeLaVergne diesel engine is installed at a cost of $82,000.
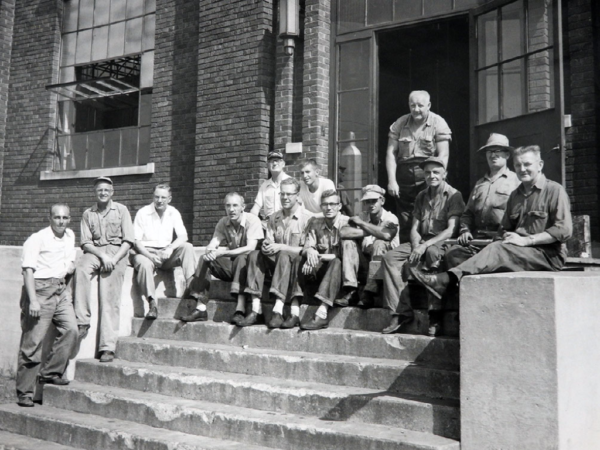

1937
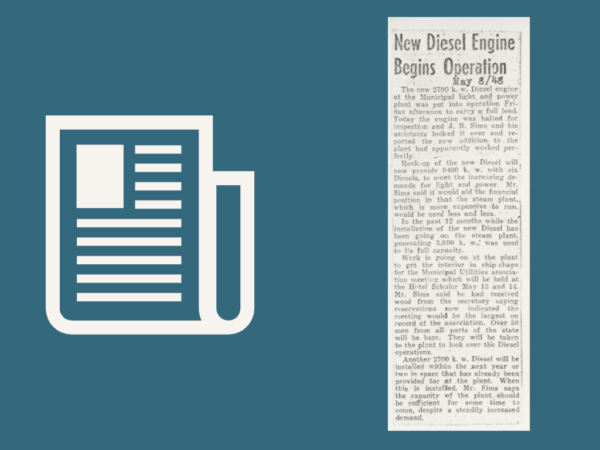
Nordberg Engine Installed – In an effort to stay ahead of load growth, the diesel plant is expanded, and a fourth engine is installed, a 2250-hp Nordberg engine. The purchase is financed in part by a WPA federal government loan. Cost $200,000, water intake pump house $19,000.

1938
Fourth consecutive rate reduction – The utility implements the first of four consecutive annual rate reductions.

1939
FREE Month of Electricity “PAID” – The utility again reduces its electric rates, this time retroactively, and gives all customers a free month of electricity by marking all April 15 thru May 15 electric bills “PAID”
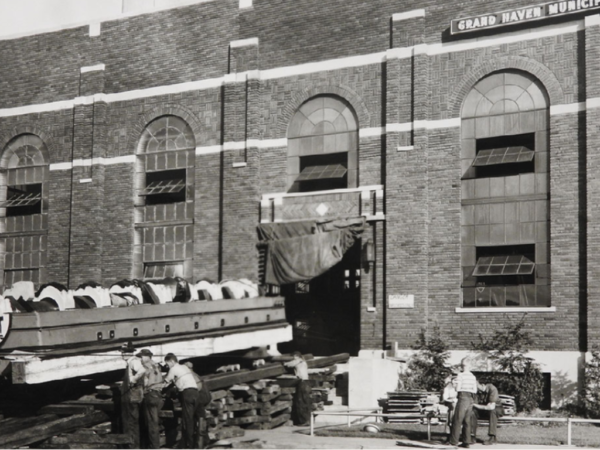

1940
Nordberg #2 Engine Installed – Continued load growth requires a fifth diesel engine. The Nordberg #2 engine with 3850-hp was installed.
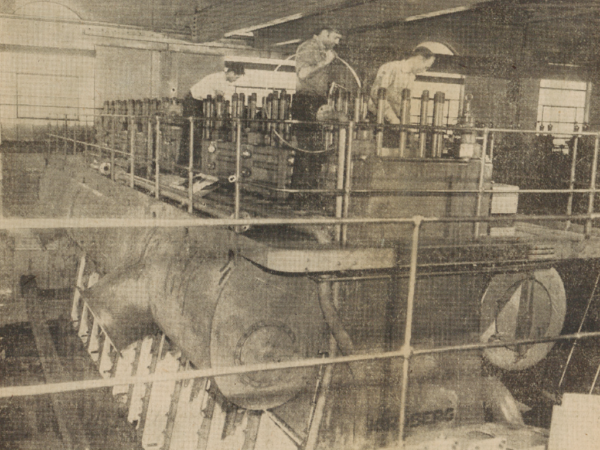
1950
Largest municipal diesel plant in the U.S. – A nine-cylinder Nordberg diesel (engine #7) is installed, at that time one of the LARGEST diesel engines built in the United States. With the addition of this engine, BLP is the largest municipal diesel plant in the U.S.

1952
Generating capability of 16,430 kilowatts – The Grand Haven Diesel Plant has a combined generating capability of 16,430 kilowatts produced by engines totaling 23,170 horsepower.
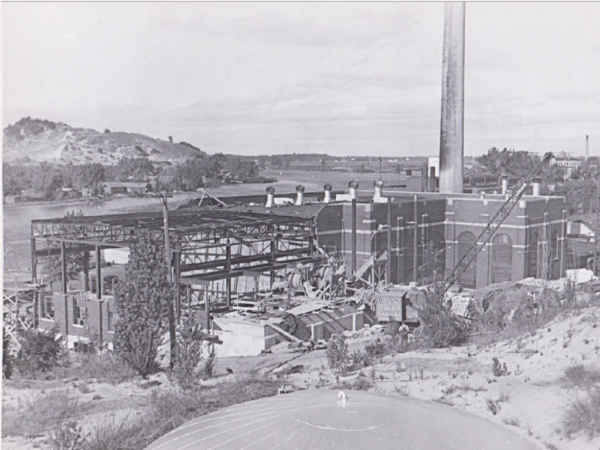

1954
$1.5 million 3-year expansion – The utility completes a $1.5 million 3-year expansion project that boosts the plant’s horsepower to more than 26,000, replacing the aging 1934 DeLaVergne engine #5 with a ten-cylinder Nordberg.
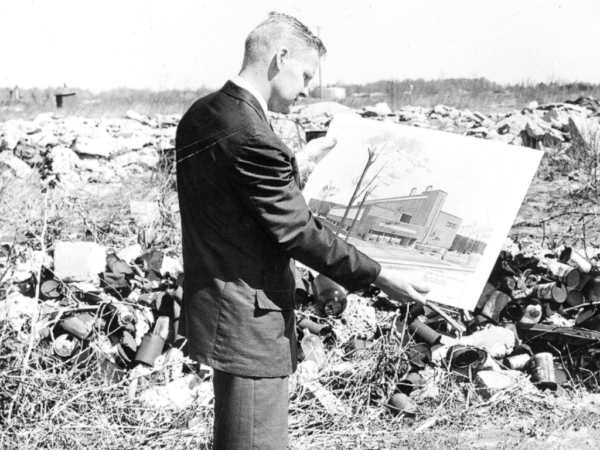

1959
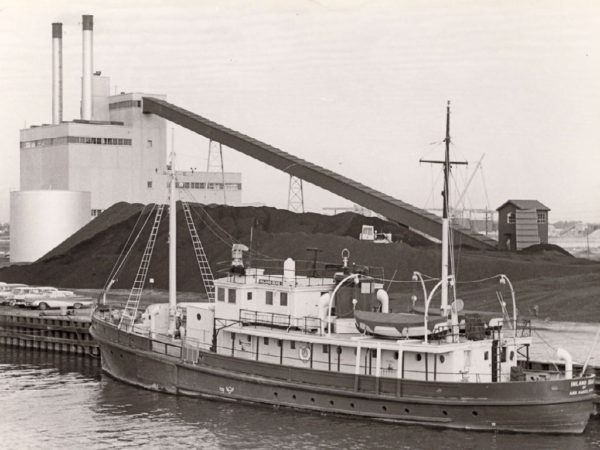
Construction begins on SIMS Generating Station Units I & II – Identical coal-fired high pressure condensing units capable of producing 10MW each installed on Harbor Island. Designed by Lutz & May, built by Elzinga & Volkers. Cost $4.95 million, completed in 1961.
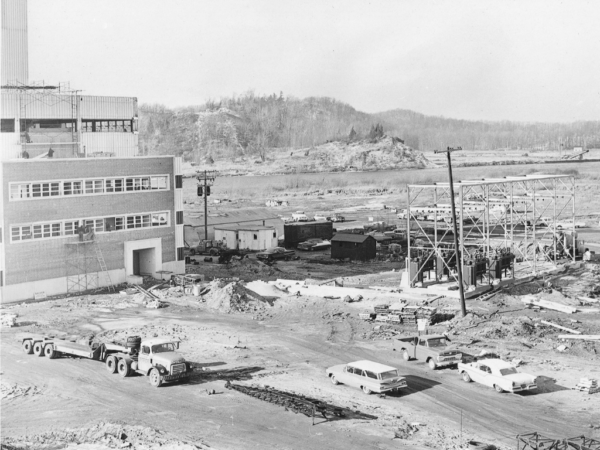

1960
Construction of SIMS Generating Station Unit I & II, built by Elzinga & Volkers, construction finished in 1961.

1980
Construction begins on SIMS Unit III – Construction begins on SIMS Generating Station, Unit III, a 65 MW
coal-fired power plant. The plant and its environmental protection equipment cost $88.5 million. The commercial operation was achieved in 1983. Unit is the first in the nation to sell gypsum byproducts.
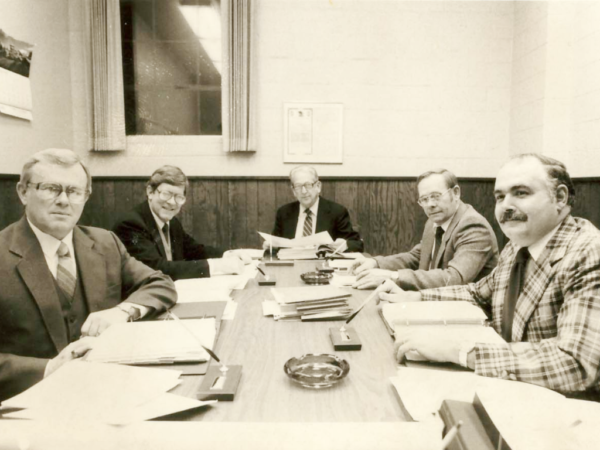

1986
SIMS Unit I & II Retired – SIMS Unit I & II are retired from service due to economic and environmental issues.
Pictured (Left to Right) – Roger Easton, Bob Atkin, Glen Eaton, Emery Holzinger, and John Montgomery.

2004
Low Nox Burners Installed – SIMS Unit III installed second-generation low Nox burners from Advanced Burner Technologies reducing emissions by 50%.
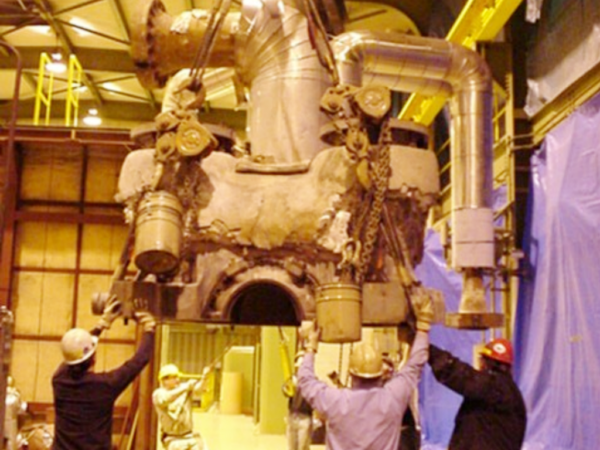

2006
SIMS Unit III Upgraded – SIMS Unit III boiler, turbine, and auxiliaries upgraded from a nominal 65 MW generator capacity to 80MW.

2008
Board approves purchase power commitment w/MPPA for up to 4 MW landfill Gas.

2009
Installed Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) – Sims Unit III selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) installed for an additional 30% reduction in Nox.

2013
Board approves purchase power commitment with MPPA for 2.4 MW Wind Generation.

May 2016
May 19, 2016 – 20 Year Purchase Power Commitment with MPPA for Huron Wind Project for 9.67% of our renewables.

August 2016
August 25, 2016, Board approves construction to remodel Service Center.

October 2016
October 4, 2016, Community Mortgage Burning Celebration held at Sims site.

August 2017
August 17, 2017, Board approves purchase power commitment with MPPA for Pegasus Wind Project (replaces Huron) for 6% of our renewables.

September 2017
September 2017 Service Center Remodel project complete.

September 2017
September 28, 2017, Phase I of the BLP’s transmission system upgrade project was complete and under budget.
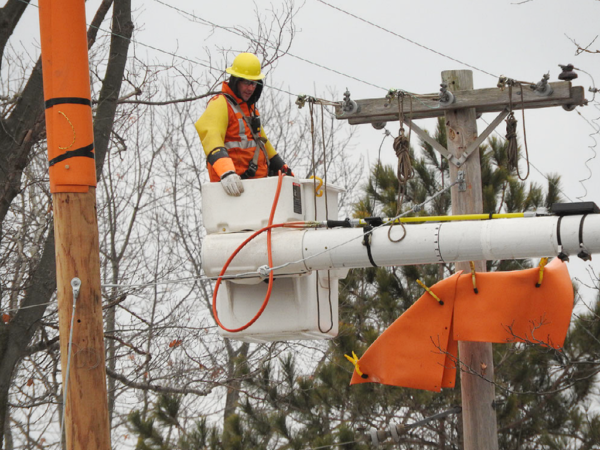

July 2018
July 27, 2018, Phase II of the GHBLP’s transmission line project is complete, which includes both the transmission and distribution portions of the project.
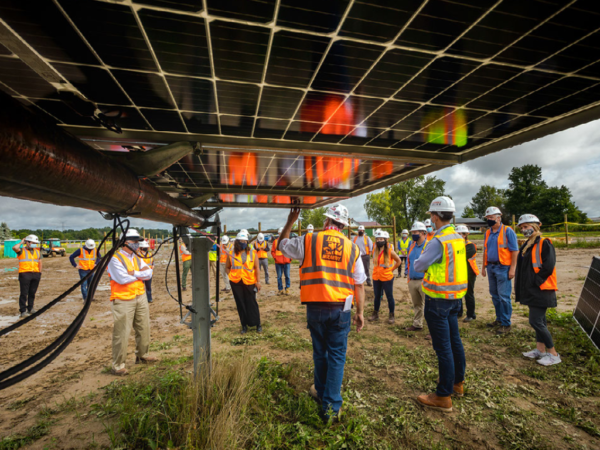

September 2018
September 20, 2018, The Board of Light & Power approves a 20-year Purchase Power Commitment with Michigan Public Power Agency for approximately 10 MWs of energy from the Assembly Solar & Energy facility

November 2018
November 11, 2018, last shipment of coal was delivered to JB Sims.

March – May 2019
March 21, 2019 – Board approves transition to NITS (Network Integration Transmission Service) on June 1, 2020.
May 16, 2019, Board approves MPPA 3-year Capacity purchase from June 1, 2020, till May 1, 2023, to comply with Michigan PA341.
May 19, 2019 – Board approves Purchase Power Commitment with MPPA for additional solar to replace Pegasus Wind Project.

June 2019
June 18, 2019, Phase III of the GHBLP’s transmission line project is complete. This phase concludes a three-year project that encompassed a complete rebuild of the GHBLP owned transmission system from Robbins Road in Grand Haven north to Sternberg Road in Fruitport Township. This transmission system rebuild is sized and designed to supply the Grand Haven area community with safe and reliable electric power for many years.

November – December 2019
November 2019 – Board approves letter of authorization with MPPA for 15-year capacity purchase for up to 8 MWs.
December 2019 – Board approves AMI contract for purchase and installation of AMI (Advanced Meter Infrastructure) equipment for a total cost of $2.3 million.
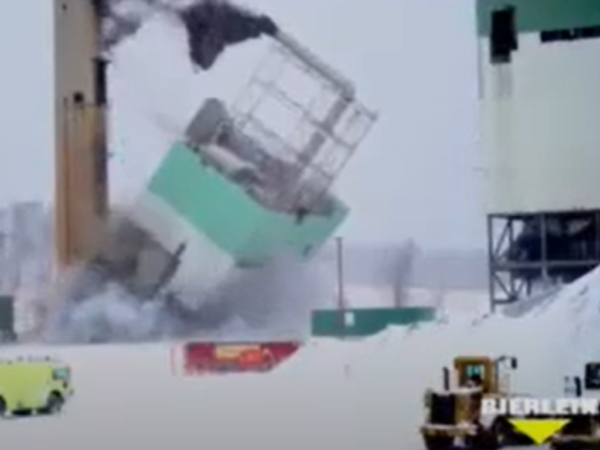
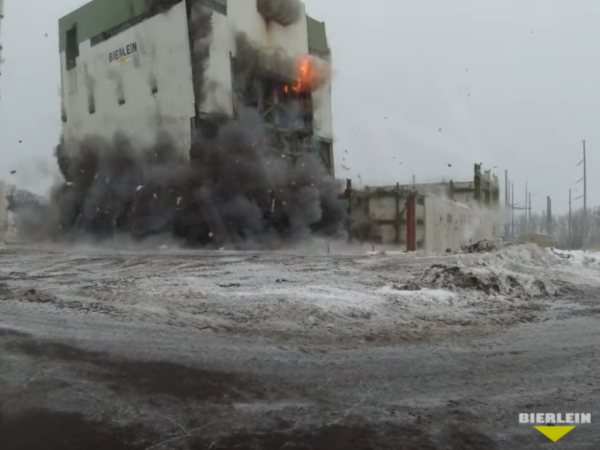
December 19, 2019, Sims’s demolition contract with Bierlein Company is approved in the amount of $5,053,333 million.
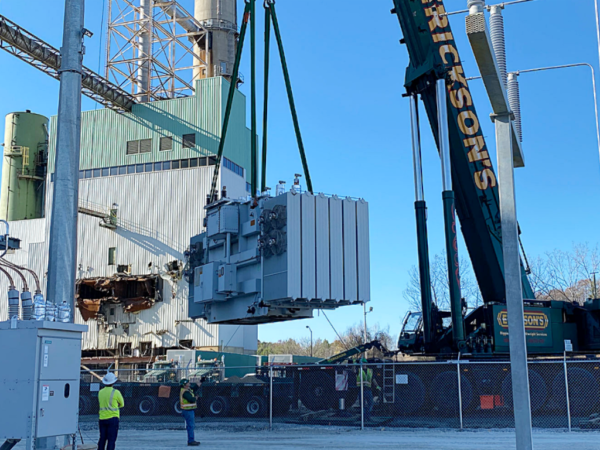

January 2020
January 16, 2020, Board approves Island Substation rebuild for a cost of $4 million.

February 2020
February 13, 2020, J.B. Sims Generating Station burned through its final pile of coal. The BLP is successfully progressing through its Strategic Plan objective to transition from primarily one fuel source to a more sustainable, economical, and diversified power supply portfolio for the community.
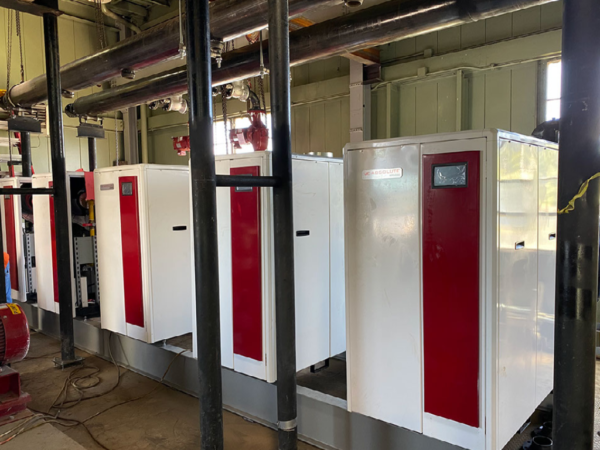

February 2020
February 20, 2020, Board approves Progressive AE to design an interim snowmelt system.

April 2020
April 2020 Due to COVID 19 Pandemic, April 2020 was the worst sales record month in the last 20 years.

June 2020
June 1, 2020, Sims Unit III and Diesel Plant retired. Utility moves to NITS (Network Integration Transmission Service).
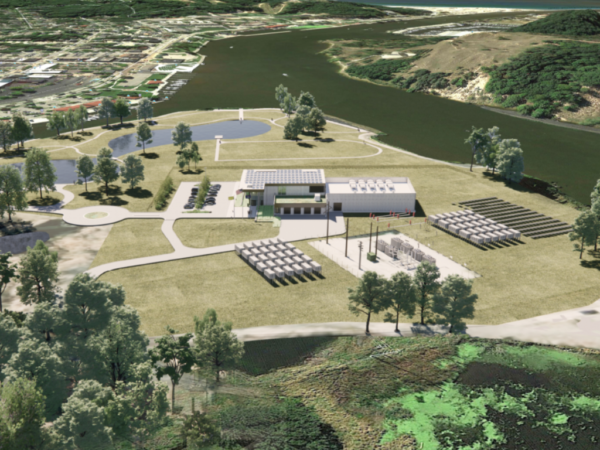

June 2020
June 18, 2020 Board approve Notice of Intent for Bond Resolution and First Supplemental Revenue Bond Resolutions.
November 6, 2020, Board-approved contracts to develop detailed design and engineering plans for an operations and technology center at the utility’s Harbor Island location. The redeveloped site would house GHBLP’s advanced distribution hub, operations staff, grid interconnection, downtown substation, and a 12.5MW combined heat and power generation facility.
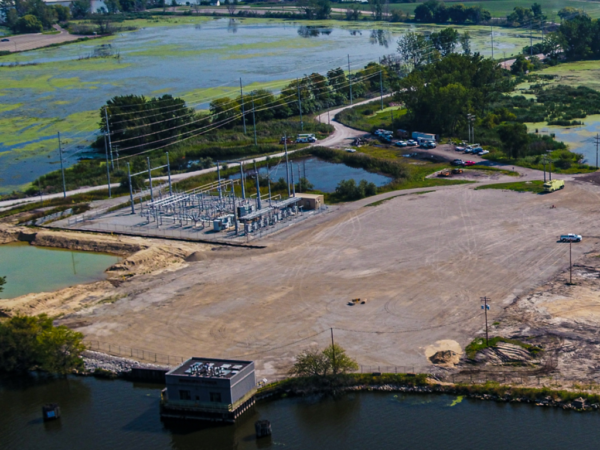

November 2020
November 5, 2020, New Island Substation is brought online.
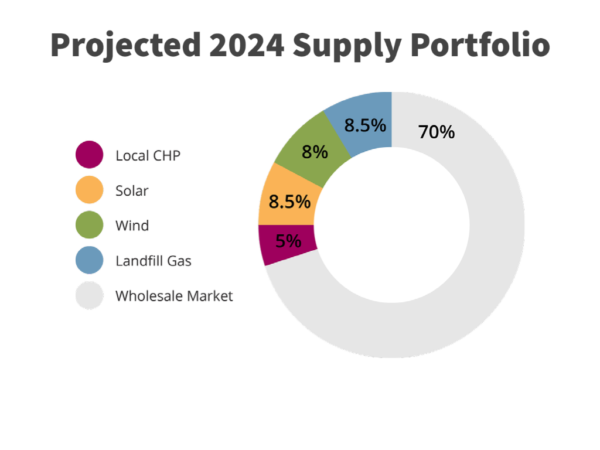
August 2021
August 2021, Board approves 5 yr. capacity purchase for approximately 15 MWs and cancels proposed 12.5 MW RICE plant project.
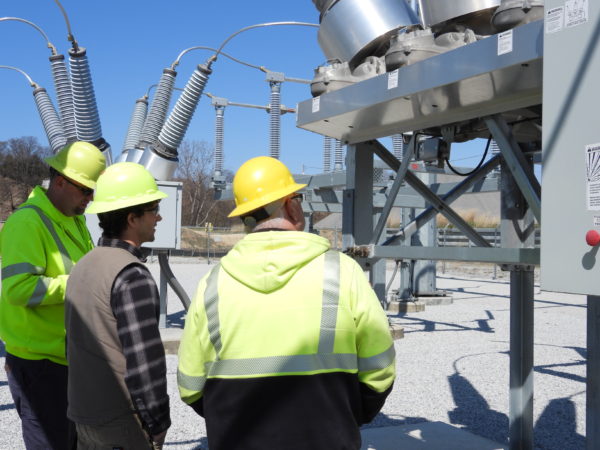

December 2021
$25 million in bonds were sold to fund demolishing the Sims power plant, conducting environmental remediation, rebuild the Harbor Island substation, and implement advanced metering infrastructure (AMI).

July 2022
The Board authorizes a $2 million contribution to the MERS Defined Benefit Plan as part of a five-year strategy to reach 100% funding.

March 2023
The Board approves a 10-year Power Purchase Commitment (PPC) with Michigan Public Power Agency (MPPA) for the BLP’s pro-rata share of MPPA’s Battery Energy Storage Systems Capacity Purchase and Sale Agreement with White Ox LLC.
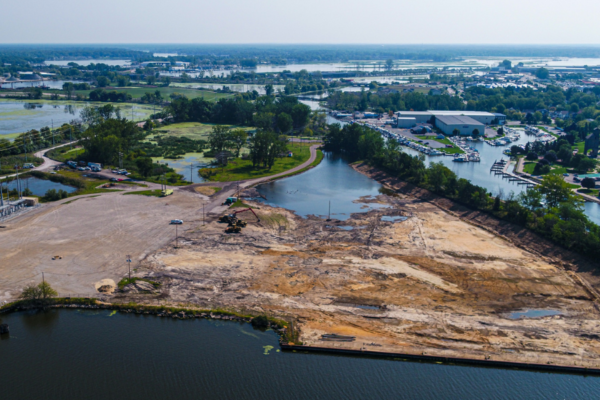

May 2023
The Board restricts reserve funds for the purpose of covering its liabilities for environmental remediation of the Sims site.